
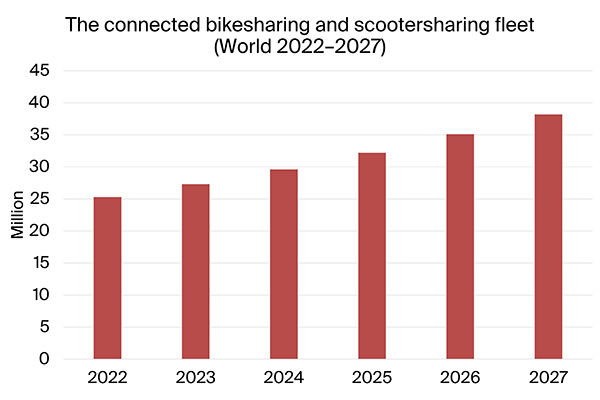
According to a new market research report from the IoT analyst firm Berg Insight, the number of micromobility vehicles available worldwide will reach 38.2 million by 2027, up from 25.3 million vehicles in 2022.
Micromobility services are defined as shared mobility services that offer short-term rentals of light vehicles such as bikes, scooters or other similar vehicles. The micromobility market has been characterized by rapid growth, a high pace of merger and acquisitions and many shutdowns of services during the past few years.
“The market is now reaching a more mature stage and operators are generally more focused on reaching profitability, which was not the case in previous years”, said Martin Cederqvist, IoT Analyst at Berg Insight.
Bikesharing is a decentralised bicycle rental service, usually focusing on short term rentals. Traditionally, most bikesharing operators have used station-based operational models. This operational model requires members to pick up and return the vehicle at any designated station within a city. In Europe and North America, station-based bikesharing is the most popular operational model. Another model that is rapidly gaining in popularity is free floating services, which enables members to pick up and drop off vehicles anywhere within a designated area. The total number of shared bikes worldwide reached an estimated 23.7 million vehicles at the end of 2022, of which a large majority are free floating bikes in China. Prominent bikesharing operators include Hellobike, Meituan Bike, Didi (Qingju), JCDecaux, Nextbike (owned by Tier), Hello Cycling, Docomo Cycle, Anywheel, Yulu, RideMovi, Bolt, Lime and Donkey Republic.
The stand-up scootersharing market has gained a lot of attention from media and investors and have grown rapidly since its inception in 2017. At the end of 2022, the number of shared stand-up scooters reached an estimated 1.5 million vehicles.
“Leading stand-up scooter operators include Bolt, Tier and Voi in Europe, Bird and Lime in North America as well as Neuron Mobility, Swing Mobility and Beam Mobility in Asia-Pacific”, said Mr Cederqvist.
The regulatory environment surrounding stand-up electric scooters is complex and varies between region, country, state and city level. Today, some cities limit the number of stand-up scooters allowed on the streets through mandatory operator licences. The cities can both restrict the number of operators allowed in the cities, but also the number of vehicles each operator is allowed to deploy. The sit-down scootersharing market has not been regulated to the same degree. At the end of 2022, the number of shared sit-down scooters in shared mobility schemes reached an estimated 120,000 vehicles. Leading sit-down scootersharing operators include Vogo and Yulu in India; Marti Technologies in Turkey; Cooltra, CityScoot, Felyx, Emmy and Check in Europe; Revel in North America as well as GoShare and WeMo in Taiwan.
Telematics has been a key element since the inception of shared micromobility services. Bikesharing infrastructure vendors provide complete solutions including telematics hardware solutions, user identification and bike locks, information kiosks as well as fleet management platforms and mobile apps.
Companies specialising in bikesharing solutions include PBSC (owned by Lyft), Lyft, Nextbike (Tier), Fifteen, Vaimoo, Youon Bike Technologies and Conneqtech. Scootersharing operators now mainly utilise factory-installed telematics systems embedded in the scooters. Shared mobility software platforms moreover comprise complete systems that can support all the operational activities of a micromobility operation ranging from management of in-vehicle equipment, fleet management, booking management, billing as well as operations supervision via dashboards and data analytics. Leading micromobility telematics solution providers include Comodule, Drover AI, Luna Systems, Invers, Teltonika, Queclink, Atom Mobility, Joyride Technologies, Wunder Mobility, Zoba, Urban Sharing and Omni Intelligent Technology.
Mr Cederqvist concluded:
“In recent years, micromobility operators have added increasingly complex telematics applications such as sidewalk riding detection as well as features ensuring parking compliance. The usage of AI and machine learning models are increasingly common in such applications.”







